
- Jul 26, 2025
From Copper to Fruit: Exploring Chile’s Diverse Export Market and Global Reach
Chile has established itself as one of the most open economies in Latin America thanks to its advantageous geographic location, varied natural resources, and robust legal and trade framework. As per Chile Export Data by Import Globals, the nation has several free trade agreements (FTAs) with major international economies, such as China, the United States, the European Union, and various Asia-Pacific countries. It is also a founding member of the Pacific Alliance. Chile's exports have increased dramatically as a result of this vast trade network, which has also made international trade a vital part of the country's GDP.
Chile's export base has grown over time, moving from copper alone to a more varied portfolio that now includes wood pulp, wine, fruits, fish products, and lithium. Nonetheless, copper still holds a dominant position and has a significant impact on its economic success. Chile's exports of copper and lithium are anticipated to become even more important in the upcoming years due to the growing demand for clean energy technology and electric vehicles worldwide. As per Chile Import Export Trade Data by Import Globals, despite global slowdowns and geopolitical concerns, Chile has been able to maintain a competitive edge in international trade thanks to its export strength and stable economic policies.
Analysis of the General Economy and its Indicators
Many people consider Chile's economy to be among the most competitive and stable in Latin America. It runs on a free-market framework backed by strong institutions, a minimal national debt, and careful budgetary control. Chile's economy has grown steadily over the years, mostly due to its robust export industry, especially in the mining sector. Additionally, as per Chile Import Custom Data by Import Globals, the nation has taken the initiative to keep inflation rates low, retain investor confidence, and put social programs in place that are meant to lessen poverty and income disparity. Inflation has been primarily kept within the 2–4% range over the past ten years thanks to the Central Bank of Chile's inflation targeting monetary policy.
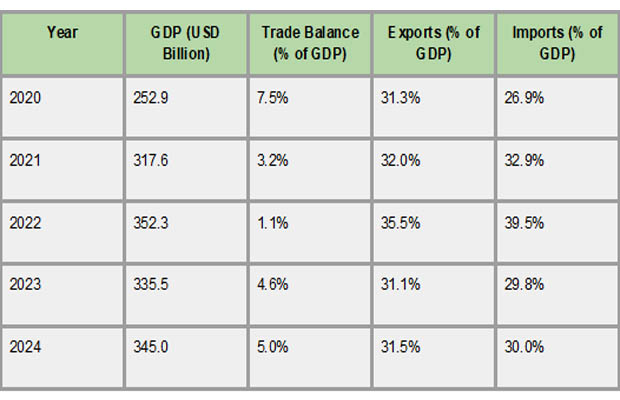
Chile's economic strengths and weaknesses are reflected in key economic indicators. The GDP is predicted to reach USD 345 billion by 2024, indicating a rebound from major world disruptions, including the COVID-19 epidemic and shocks to commodity prices. Over 30% of the nation's GDP comes from exports, underscoring its reliance on international trade. Since the pandemic, as per Chile Import Trade Analysis by Import Globals, Chile's unemployment rate has been stable at 7–8%, while investor-friendly policies have kept foreign direct investment stable. Nonetheless, the economy is still vulnerable to outside threats like fluctuating commodity prices, particularly those of copper and lithium, and worldwide economic downturns, which can have a big effect on export earnings and overall expansion.
Export Data Review
Chile's export industry showed growth and resilience between 2020 and 2024, despite international obstacles like the COVID-19 pandemic and volatile commodity prices. Exports were worth about USD 74.08 billion in 2020, which reflected the pandemic's early effects. However, as per Chile Export Data by Import Globals, there was a notable comeback in exports by 2021, when they reached USD 94.68 billion. With exports hitting USD 98.56 billion in 2022, the rising trend persisted. Strong results in the mining, agricultural, and forestry industries propelled exports to reach USD 100.16 billion in 2024 after a minor drop to USD 94.94 billion in 2023.
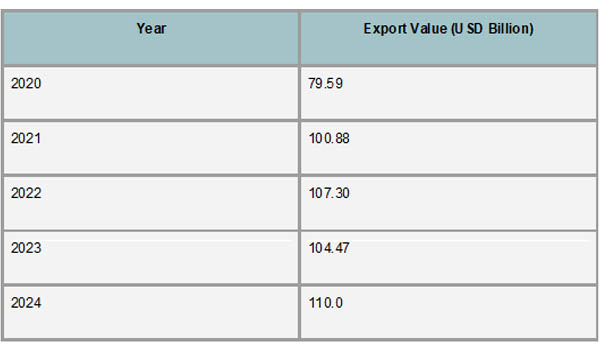
With a 9.5% increase in 2024 to USD 52.28 billion, the mining industry continued to be the mainstay of Chile's exports. Record shipments of gold, copper concentrates, and copper cathodes drove this expansion. As per Chile Import Data by Import Globals, significant increases were also seen in agricultural exports; fresh fruit shipments reached USD 6.97 billion, a 20.3% rise over 2023. Wine exports totaled USD 1.51 billion, up 6.4%, while the forestry sector contributed USD 2.12 billion, up 2.1%. These numbers highlight Chile's diverse export base and its capacity to adjust to the needs of international markets.
Diverse Export Categories of Chile’s Exports
Although Chile's export economy is diverse, the mining industry nevertheless plays a major role in driving it. With almost half of all export earnings coming from copper, it continues to be the most important export. As per Chile Import Trade Statistics by Import Globals, Chile is a major source of lithium and the world's largest producer of copper, two elements essential to the transition to renewable energy and global infrastructure. The nation exports substantial amounts of iodine and molybdenum in addition to minerals. With a combined export value of more than USD 48 billion in 2024, these mineral-based exports are classified under HS Codes 26 (ores, slag, and ash) and 74 (copper and goods thereof).
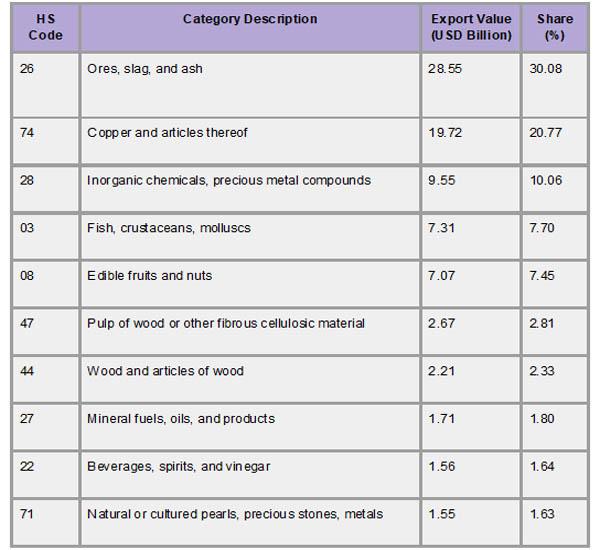
Chile has developed robust industries in forestry, aquaculture, and agriculture in addition to mining. It is one of the top exporters of fresh fruits (HS Code 08), especially apples, blueberries, cherries, and grapes. Another crucial market is seafood (HS Code 03), which includes trout and salmon, particularly for the US and Japanese markets. Wood pulp and lumber (HS Codes 44 and 47) are contributions from the forestry industry, while wine (HS Code 22) and other beverages have become well-known worldwide, particularly in North America and Europe. In addition to increasing Chile's economic resilience, as per Chile Import Shipment Data By Import Globals, this diversity creates opportunities for trade alliances across continents and industries.
Major Export Destinations
China is Chile's top commercial partner, and the country's export economy is mostly focused on the Asia-Pacific area. About USD 30.75 billion worth of Chilean exports went to China in 2024, making up roughly 38% of the country's total exports. As per Chile Import Export Trade Analysis by Import Globals, China's need for Chilean copper and lithium, which are vital to its industrial and renewable energy sectors, is a major factor in this strong economic relationship. With exports of USD 12.3 billion, or around 15% of Chile's total exports, the US comes in second as a destination for Chile's exports. Minerals, agricultural goods, and services are all included in this varied commerce, which has seen a sharp rise in U.S. imports of Chilean lithium to support green energy projects.
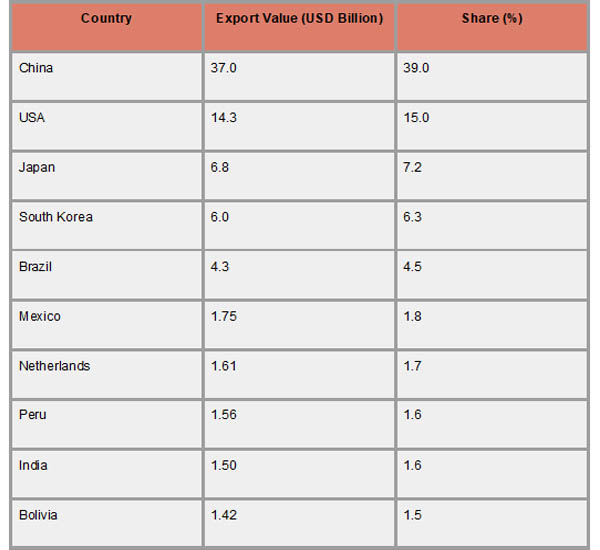
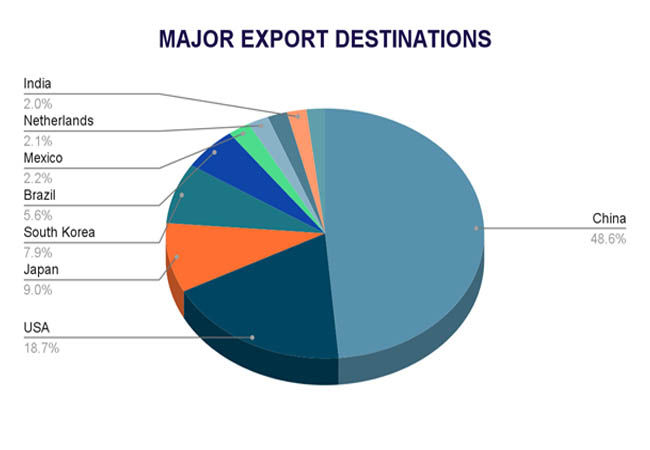
Brazil, South Korea, and Japan are important export destinations for Chile. Exports to South Korea and Brazil totaled USD 5.21 billion and USD 3.51 billion in 2024, respectively, while exports to Japan totaled USD 5.48 billion. Chilean agricultural products, seafood, and copper are the main imports into these nations. With exports of USD 1.18 billion in 2024, as per Chile Export Import Global Trade Data by Import Globals, India has become a major and expanding market. To increase exports of fruits, wines, and meats and push for lower tariffs to improve market access, Chile is actively working to improve commercial relations with India.
Strategic Consequences
Mining Dominance: Chile's economy is highly dependent on mining, especially copper, which leaves it vulnerable to changes in the price of commodities globally.
Diversification Efforts: To lessen reliance on mining, the government is encouraging diversification into the forestry, renewable energy, and agricultural industries.
Trading Relations: Chile's economy is stable due to its strong trading relations with China and the United States, but it is also vulnerable to geopolitical threats.
Sustainable Practices: A focus on sustainable mining and agricultural methods is essential for long-term economic and environmental well-being.
Chile's strong reliance on exports, particularly in the mining industry, has both strengthened and exposed the country's economy. As per Chile Import Export Global Data by Import Globals, Chile is now at the center of vital supply chains and makes a substantial amount of money thanks to the worldwide transition to green energy, which has increased the value of Chilean copper and lithium. But this focus on exports also makes the economy more susceptible to changes in international markets. Chile's trade balance and GDP growth might be significantly impacted by a steep drop in copper prices or a reduction in demand from a significant trading partner like China, which alone accounts for over 40% of Chile's exports. Furthermore, Chile's economy is vulnerable to interruptions during international trade disputes or global conflicts due to its dependence on other countries, which exposes it to geopolitical risks.
Trade Predictions
The export outlook for Chile in 2025 is a complicated picture that is influenced by both possibilities and difficulties. In 2024, the country's export value was $100.16 billion, and early 2025 data showed that it was off to a good start. However, due to global economic concerns and a decline in demand from big users like China, the government has lowered its 2025 copper price projection downward to $3.90 to $4.00 per pound. Although production in the lithium sector is expected to rise to 305,000 tons, there will likely be a global excess, which might drive down prices. Chile is well-positioned to sustain strong trade performance despite these challenges, thanks to its diverse export portfolio, which includes forestry, services, and agriculture.
Conclusion
In summary, Chile's export-oriented economy, which is supported by a wealth of natural resources and a diverse variety of goods beyond mining, such as forestry and agriculture, continues to be a pillar of the country's prosperity. Although the nation enjoys robust trade relations, especially with China and the US, its significant reliance on exports of copper and lithium exposes it to geopolitical risks and fluctuations in the world market. In the future, maintaining economic growth and resilience in a more complex global trade environment will depend heavily on Chile's capacity to manage shifting commodity prices, enter new markets, and increase trade diversification.
If you are looking for detailed and up-to-date Chile Import Data, You Can Contact Import Globals.
FAQs
Que. What are Chile’s main export products?
Ans. Chile’s exports are dominated by copper and lithium, which are essential for the global electronics and green energy industries. Other major export products include fresh fruits, seafood (especially salmon), wood pulp, and wine.
Que. Which countries are the largest importers of Chilean goods?
Ans. China is Chile’s largest export destination, accounting for nearly 40% of exports, followed by the United States, Japan, South Korea, and Brazil. Emerging markets like India are also becoming increasingly important.
Que. How does Chile’s reliance on copper and lithium exports impact its economy?
Ans. While copper and lithium exports bring significant revenue and global importance, heavy dependence on these commodities exposes Chile to risks from price volatility and demand fluctuations, especially from major trading partners like China.
Que. What strategies is Chile using to diversify its export markets?
Ans. Chile is actively pursuing trade agreements and partnerships beyond its traditional markets, focusing on expanding exports to emerging economies such as India. The country is also diversifying its export portfolio by strengthening the agriculture, forestry, and service sectors.
Que. Where to obtain detailed Chile Export Data?
Ans. Visit www.importglobals.com or email info@importglobals.com for more information on up-to-date Chile Export Data.
