
- Aug 07, 2025
Lesotho's Export Landscape: An Overview and Strategic Outlook
Through preferential trade agreements like the African Growth and Opportunity Act (AGOA), as per Lesotho Export Data by Import Globals, Lesotho has established a niche in international markets despite its small size and geographic limitations. Employment and GDP contribution are significantly influenced by the nation's manufacturing industry, which is mostly concentrated on producing clothing for export. However, the economy is susceptible to external shocks due to its strong reliance on a small number of product categories and restricted trading partners.
Global economic trends, regional trade conditions, and changes in the policy of major partners, most notably the United States and South Africa, have all influenced Lesotho's export performance in recent years. Lesotho's exports fluctuated between 2020 and 2024 as a result of many causes, including logistical difficulties, shifting tariff regimes, and COVID-19 disruptions. As per Lesotho Import Data by Import Globals, highlighting important economic indicators, trade performance, partner analysis, product categories, and the strategic orientation required to ensure a stable economic future, this blog delves deeply into Lesotho's export environment.
General Economic Indicators
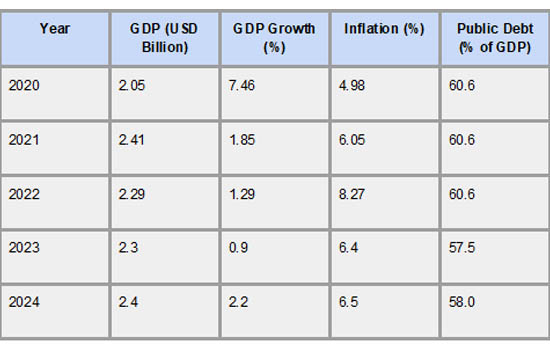
The 2020–2024 economic statistics for Lesotho show both structural vulnerabilities and resilience. Due mostly to the COVID-19 epidemic, which affected both internal and international trade, the nation had a severe downturn in 2020, with a GDP decline of -7.46%. As per Lesotho Import Export Trade Data by Import Globals, due to growing food and fuel prices, inflation rates were low but indicated an upward tendency, reaching a peak of over 8% in 2022. As a result of the government borrowing to stabilize the economy during difficult times, public debt was approximately 60% of GDP. Notwithstanding these obstacles, the economy started a gradual recovery in 2021, with modest growth bolstered by more government investment and better external demand.
However, the formal job market is still small and dominated by the government and textile sectors, and unemployment has been high for a long time, it is estimated to be over 16.9%. As per Lesotho Import Customs Data by Import Globals, Lesotho is vulnerable to external shocks like changes in trade policy or swings in global demand since its economic growth has been heavily reliant on a small number of industries, namely textile exports and remittances. To promote inclusive and resilient development in the future, sustained growth will require structural reforms, more investment, and more integration into regional value chains.
Lesotho's Export Data (2020–2024)
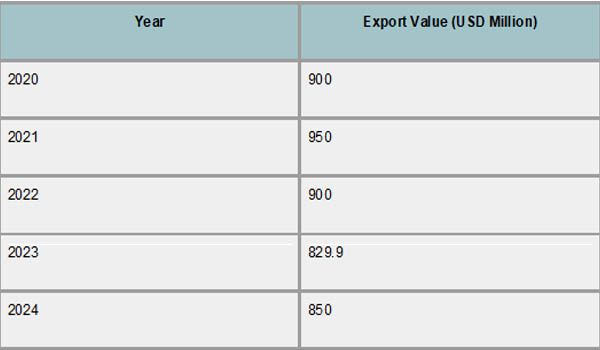
The export performance of Lesotho from 2020 to 2024 demonstrates a pattern of slow recovery after the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 caused significant interruptions. As per the Lesotho Import Trade Analysis by Import Globals, although they fluctuated, exports, which in 2020 were valued at about USD 900 million, continued to be a vital component of the national economy. Export values declined as a result of the pandemic's effects on international supply chains and decreased demand for textiles, the nation's principal export. However, Lesotho's exports increased gradually as trade logistics improved and markets started to reopen, peaking at about USD 950 million in 2021 before leveling off at USD 850–900 million in the years that followed.
Notwithstanding its general durability, the export industry had to contend with issues like shifting global trade regulations and competition from other low-cost manufacturers. As per Lesotho Export Data by Import Globals, because it generates a large portion of export earnings, the textile sector was especially susceptible to changes in tariffs and interruptions in supply. Additionally, even though their volume was lower, the nation's diamond exports brought some diversification and added to the export basket. To create a more stable and sustainable trade profile, Lesotho must diversify its products and markets and increase the size of its export base, according to export data from 2020 to 2024.
Major Export Partners
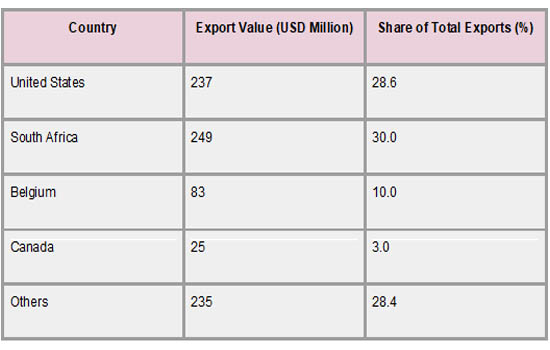
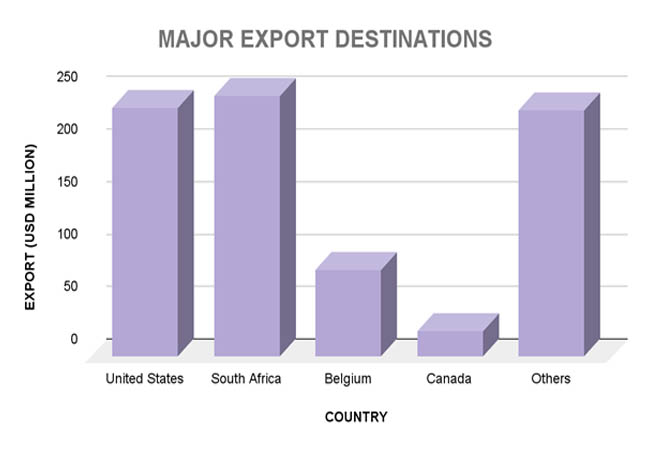
A small number of important trading partners have a significant impact on Lesotho's export environment, with South Africa and the United States being its top export destinations. As per Lesotho Import Data by Import Globals, because of the African Growth and Opportunity Act (AGOA), which gives Lesotho's textile and apparel exports preferential access, the United States continues to be the largest single market. Nearly 29% of Lesotho's total exports in 2023 went to the United States, demonstrating the vital significance this market plays in maintaining the country's industrial sector and jobs. About 30% of Lesotho's exports, including manufactured goods and diamonds, are also absorbed by South Africa, the country's closest neighbor and biggest commercial partner in the region.
Canada and Belgium are other significant export partners, albeit they provide a far smaller contribution to diversification. Canada imports a range of manufactured goods, including textiles, while Belgium's position is mostly associated with the diamond trade. Nevertheless, as per Lesotho Import Trade Statistics, because of its dependence on a small number of important trading partners, Lesotho's economy is susceptible to outside shocks like shifts in trade regulations or downturns in these nations' economies. To reduce risks, boosting intra-African trade and trade linkages with emerging countries through programs like the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) may present fresh chances for economic expansion.
Major Export Product Categories
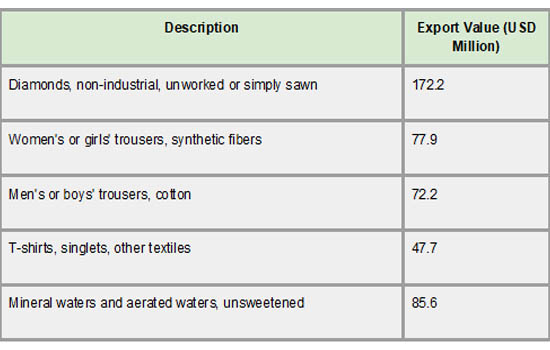
As the foundation of its manufacturing sector, textiles and clothing make up the majority of Lesotho's export portfolio. Men's and women's pants, T-shirts, and other clothing items, mainly composed of cotton and synthetic materials, are important product categories. As per Lesotho Import Shipments Data by Import Globals, the substantial export earnings that these textile items have continuously produced demonstrate Lesotho's competitive edge in the production of clothing for global markets, particularly the US. Preferential trade agreements have aided in the sector's expansion by giving Lesotho duty-free access, which is essential for preserving its export competitiveness.
Together with textiles, diamonds are an essential export that makes up a sizable portion of Lesotho's foreign exchange profits. Unworked or simply sawn diamonds are strategically important, drawing foreign investment and providing opportunities for value addition through downstream processing, despite their smaller bulk compared to textiles. As per Lesotho Import Export Trade Analysis By Import Globals, Mineral waters and aerated waters are other exports that demonstrate diversification attempts despite their low value. All things considered, the export concentration in a small number of product categories indicates the need for more diversity to lower economic vulnerability and promote sustainable growth.
Strategic Implications
Because of its strong reliance on textile exports and small trading partners, Lesotho's economy is particularly vulnerable to external shocks such as supply chain interruptions, changes in tariffs, and volatility in international markets. Lesotho must immediately diversify its export goods and target markets to strengthen its economy, as evidenced by the recent hike in tariffs by major markets. As per Lesotho Export Import Global Trade Data by Import Globals, reliance on a limited export base can be lessened by investing in value addition, particularly in industries like diamond processing, and fortifying regional trade relations through accords like the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA). Lesotho can better withstand global uncertainty and provide its people with possibilities for sustainable prosperity by expanding its economic activity and strengthening its integration into regional value chains.
Conclusion
In summary, Lesotho’s export sector remains a crucial pillar of its economy, driven primarily by textiles and diamonds. While the country has shown resilience amid global challenges from 2020 to 2024, its heavy dependence on a few products and key markets leaves it vulnerable to external shocks. Moving forward, strategic diversification of export products and expansion into new markets, coupled with stronger regional trade integration and investment in value addition, will be essential for sustainable economic growth. As per Lesotho Import Export Global Data, by addressing these challenges proactively, Lesotho can build a more robust and inclusive economy that offers greater stability and prosperity for its people.
If you are looking for detailed and up-to-date Lesotho Export Data, You Can Contact Import Globals.
FAQs
Que. What are Lesotho's main exports?
Ans. Lesotho primarily exports textiles (clothing) and diamonds.
Que. Who are Lesotho's major trading partners?
Ans. The United States, South Africa, and Belgium are among Lesotho's top export destinations.
Que. How did the U.S. tariff affect Lesotho's economy?
Ans. The 50% tariff imposed by the U.S. in 2025 significantly impacted Lesotho's textile exports, threatening jobs and economic stability.
Que. What steps can Lesotho take to diversify its exports?
Ans. Lesotho can explore new markets, invest in different sectors, and add value to its existing products to diversify its export base.
Que. Where to obtain detailed Lesotho Import Data?
Ans. Visit www.importglobals.com or email info@importglobals.com for more information on up-to-date Lesotho Import Data.
