
- Aug 06, 2025
Global Trade of Solar Water Pumps: Trends, Types, Trade Hubs & Forecast
Conventional irrigation techniques generally rely significantly on fuel or electricity-powered pumps, which are expensive, harmful to the environment, and usually unavailable in isolated rural locations.
As per Solar Water Pumps Export Data by Import Globals, by using renewable solar energy, solar water pumps present a viable substitute that offers a dependable and environmentally responsible supply of water for animals and crops. This change helps farmers sustain crop yields and secure livelihoods in the face of shifting environmental conditions, in addition to conserving valuable fossil fuels.
Additionally, the drive for sustainable irrigation is in line with international initiatives to mitigate climate change and encourage the use of clean energy. As per Import Data by Import Globals, to lower carbon emissions and provide access to water in disadvantaged areas, governments and organizations around the world are investing more and more in solar water pump technologies. By minimizing operating expenses and reliance on unstable power networks, these pumps enable smallholder farmers and promote food security and agricultural resilience. As a result, solar water pumps are helping to propel the global shift to more sustainable and environmentally friendly farming methods.
What Are Solar Water Pumps?
A solar water pump is a machine that uses solar energy to move water from wells, rivers, or boreholes for home, agricultural, or livestock uses. As per Solar Water Pumps Import Export Trade Data by Import Globals, solar water pumps are a clean, renewable, and affordable alternative to traditional pumps that run on electricity or fuel. They do this by using electricity produced by solar panels. They offer a sustainable means of guaranteeing a steady supply of water while minimizing reliance on fossil fuels and greenhouse gas emissions, making them particularly useful in isolated or off-grid locations with limited access to dependable power. Solar water pumps use solar energy to draw water from boreholes, rivers, or wells. They consist of the following main components:
Solar Panels: Capture sunlight to generate electricity.
Controller: Regulates the power and protects the system.
Electric Motor: Powers the pump.
Pump: Draws and delivers water.
Solar Panels: The key component of a solar water pump system is solar panels. They are composed of photovoltaic (PV) cells, which use the photovoltaic effect to directly turn sunlight into electricity. As per Import Custom Data by Import Globals, the entire system is powered by direct current (DC) electricity produced by the solar panels' cells when sunlight strikes them. The pump's power needs and the amount of sunshine present at the site determine the size and quantity of panels.
Controller: The controller acts as the system’s brain, managing and regulating the flow of electricity from the solar panels to the pump. It ensures that the pump receives the right amount of power, preventing damage caused by fluctuations in sunlight or electrical surges. Some advanced controllers also protect against overheating, short circuits, and overvoltage. Additionally, they may include features like automatic shut-off during low water levels to protect the pump.
Electric Motor: The electric motor transforms solar panel electrical energy into mechanical energy. The pump's working components are propelled by this mechanical energy to raise and move water. As per Import Trade Analysis by Import Globals, the motor may be powered directly by the solar panels, or it may be an alternating current (AC) motor that needs an inverter to convert DC to AC, depending on the system. In general, DC motors are more effective and more appropriate for solar power applications.
Pump: The part that physically transports water from its source, a borehole, well, or river, to its intended destination, such as storage tanks or agricultural fields, is called a pump. Surface pumps are used for shallow water sources, whereas submersible pumps can function at deeper depths. Pump designs differ based on their intended usage. How much water the pump can supply and from what depth depends on its capacity, which is expressed in terms of flow rate and head (the height at which water is lifted).
Types of Solar Water Pumps
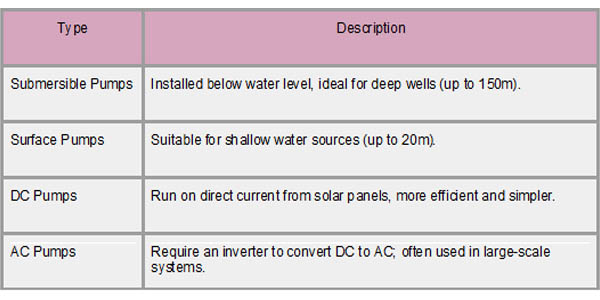
Surface pumps and submersible pumps are the two primary varieties. Installed underwater in deep wells or boreholes, submersible pumps are made to raise water from deeper depths, typically as much as 150 meters. As per Export Data by Import Globals, conversely, surface pumps are above ground and can be used to pump water from shallow sources, which are usually found less than 20 meters below the surface. Furthermore, solar pumps can be powered by either alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC); AC pumps use an inverter to convert DC to AC, which enables higher power and is frequently used for larger applications, while DC pumps are simpler and more energy-efficient and run directly on electricity from solar panels.
Quality and Performance Standards
For solar water pumps to be dependable, effective, and long-lasting in a variety of environmental circumstances, quality and performance criteria are essential. The energy efficiency ratio (the amount of water pumped per unit of energy), longevity (many are built to last 10 to 25 years), and robustness against water and dust (typically indicated by IP ratings) are the main criteria used to evaluate high-quality pumps. As per Import Data by Import Globals, strict safety and performance requirements are met by the pumps thanks to regional approvals like India's MNRE rules or international certifications like IEC standards and Solar Keymark. These pumps are reliable for farmers and communities that depend on sustainable irrigation solutions because of features like corrosion resistance, robust motor operation, and sophisticated controls that contribute to consistent performance.
Product Analysis
Key Market Drivers:
Agricultural modernization in developing countries is increasing demand for efficient irrigation solutions.
The growing global adoption of renewable energy supports solar pump deployment.
Declining costs of photovoltaic (PV) panels and lithium-ion batteries make solar pumps more affordable.
Government subsidies and incentive programs (e.g., India’s PM-KUSUM, USAID projects in Africa) boost market growth.
Market Challenges:
High initial investment cost can be a barrier for small-scale farmers.
Maintenance and technical support are often difficult in remote and rural areas.
Limited awareness and technical knowledge among end-users hinder widespread adoption.
Major Manufacturing Firms and Hubs
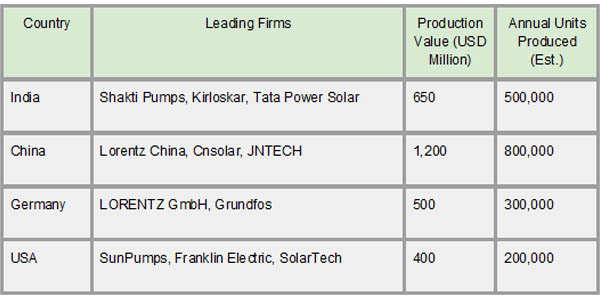
Countries with robust renewable energy sectors and well-established technical industries are home to major solar water pump production hubs. With firms like Lorentz China and Cnsolar in China and Shakti Pumps and Kirloskar in India producing in significant quantities to satisfy both local and foreign demand, India and China dominate the global market. As per Import Trade Statistics by Import Globals, another important player is Germany, which is home to well-known companies like Grundfos and LORENTZ GmbH, which are recognized for producing high-quality, cutting-edge pumps. Businesses in the US that concentrate on innovation and serve specialized markets include SunPumps and Franklin Electric. Because of their strong supply chains, government assistance, and highly qualified workforce, these hubs can manufacture solar pumps at affordable prices while consistently enhancing their durability and efficiency.
Manufacturing Process of Solar Water Pumps
Several crucial steps are involved in the production of solar water pumps to guarantee effectiveness, robustness, and dependable operation:
Design and Engineering: Water source, depth, and power requirements are taken into account when creating system specifications.
Production of Solar Panels: Photovoltaic cells are manufactured, joined together to form panels, and their energy production is examined.
Pump and Motor Assembly: Pump parts (shafts, impellers) and electric motors are produced and combined.
System Integration: A single unit is created by combining solar panels, controllers, motors, and pumps.
Quality Testing: Measurements of flow rate, energy efficiency inspections, and evaluations of environmental durability are examples of performance testing.
Distribution & Packaging: Completed goods are safely packed before being sent to both domestic and foreign markets.
Major Exporter Countries of Solar Water Pumps
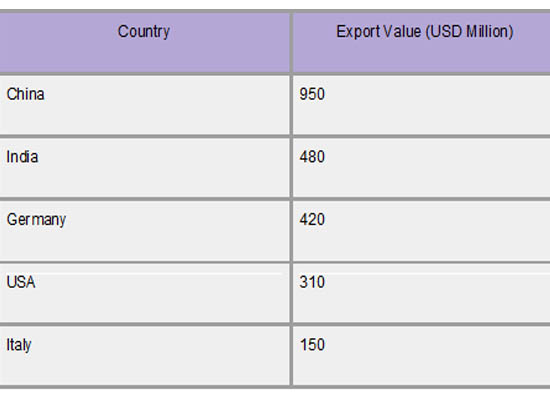
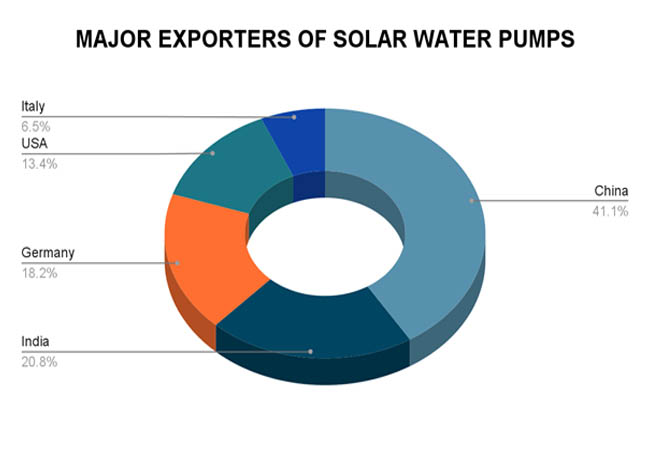
Countries with robust manufacturing capacities and developed renewable energy sectors are the top exporters of solar water pumps. Due to its extensive production capacity and economical manufacturing methods, China leads the world export market. India, which gains from government programs supporting solar technologies, is not far behind. As per Import Shipment Data by Import Globals, another significant exporter is Germany, which primarily serves the European and growing markets with its superior and cutting-edge solar pumping equipment. The US contributes significantly as well, emphasizing items for niche markets that are driven by innovation. Other suppliers, such as Italy, provide high-end, specialized solar pump types. These nations collectively meet most of the world's demand, which propels the expansion of sustainable irrigation technologies globally.
Major Importer Countries of Solar Water Pumps
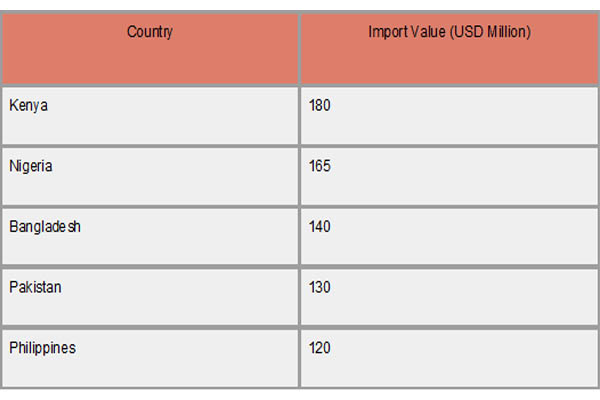
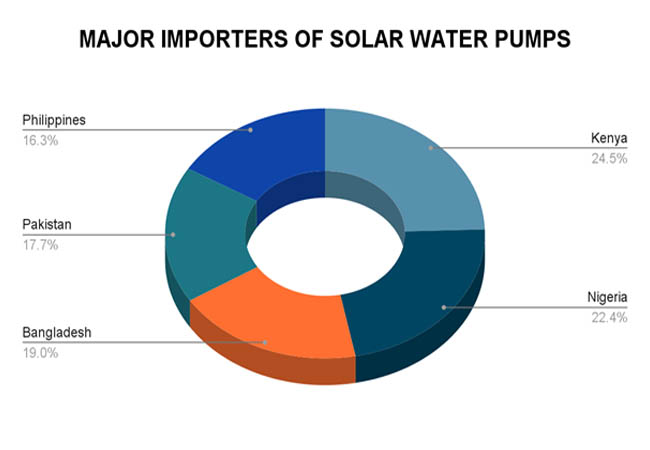
Africa and South Asia, two regions with a strong reliance on agriculture and limited access to dependable electricity, are the main importers of solar water pumps. As per Import Export Trade Analysis by Import Globals, they use solar pumping technologies to improve irrigation and water availability in rural regions. Nations like Bangladesh, Nigeria, and Kenya are leading importers. Due to government initiatives and foreign aid projects targeted at enhancing water security and advancing renewable energy, Pakistan and the Philippines also constitute sizable markets. To assist smallholder farmers, lessen dependency on diesel pumps, and promote sustainable agricultural development in off-grid regions, these importers mostly rely on affordable and effective solar pumps.
Strategic Implications of Solar Water Pump Trade
The international commerce in solar water pumps has important strategic ramifications for rural development, environmental sustainability, and energy security. As per Export Import Global Trade Data by Import Globals, pumps contribute to reducing reliance on fossil fuels and traditional electrical grids, which lowers greenhouse gas emissions and advances efforts to mitigate climate change by making clean and dependable water pumping solutions more accessible. Through manufactured exports and technological innovation, this trade helps exporting nations' renewable energy sectors grow, provide jobs, and accelerate economic growth. Importing countries gain from increased agricultural output, better water management, and increased resistance to drought and water scarcity—all of which are essential for reducing poverty and ensuring food security. International cooperation and investment in solar pump technology can also support global clean energy transitions, improve geopolitical relations, and promote sustainable development.
Forecast Trends (2025–2030)
Solar water pumps are becoming more affordable and efficient due to technological advancements like the creation of direct current (DC) surface suction pumps, which also makes them more accessible to small-scale farmers in rural areas. Furthermore, the combination of remote monitoring systems and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies is increasing operational dependability and efficiency, which enables improved system management. As per Import Export Global Data by Import Globals, the expansion of solar water pump systems and sustainable practices will probably become more important as the industry develops to satisfy the world's expanding energy and water demands.
Conclusion
In conclusion, solar water pumps represent a transformative solution at the intersection of sustainable energy and efficient water management. As the global demand for clean and affordable irrigation technologies grows, these pumps offer significant benefits, including reduced reliance on fossil fuels, lower operational costs, and enhanced agricultural productivity, especially in remote and off-grid regions. With continuous technological advancements, supportive government policies, and increasing market adoption, solar water pumps are set to play a vital role in promoting environmental sustainability and food security worldwide. Investing in this technology not only addresses immediate water challenges but also contributes to long-term climate resilience and rural development.
If you are looking for detailed and up-to-date Solar Water Pumps Export Data, You Can Contact Import Globals.
FAQs
Que. What is a solar water pump used for?
Ans. It is used to pump water using solar energy, mainly for irrigation, livestock watering, and drinking water in rural areas.
Que. Which countries export the most solar pumps?
Ans. China, India, Germany, the USA, and Italy.
Que. Why are solar pumps ideal for agriculture?
Ans. They reduce dependency on diesel, lower operational costs, and work well in off-grid areas.
Que. What challenges do solar pump markets face?
Ans. High initial costs, lack of awareness, and maintenance issues in remote areas.
Que. What is the future of solar water pumps?
Ans. The future is bright with AI, IoT integration, and increased adoption in Africa and Asia due to government and NGO interventions.
Que. Where to obtain detailed Soalr Water Pumps Import Data?
Ans. Visit www.importglobals.com or email info@importglobals.com for more information on up-to-date Soalr Water Pumps Import Data.
