
- Jul 28, 2025
Republic of the Congo's Import Landscape: Trends, Partners, and Strategic Outlook
To lessen its significant reliance on oil earnings, the nation has spent the last ten years concentrating on infrastructural development and economic diversification. Its import trends have been greatly impacted by this growth drive, as evidenced by the growing demand for energy items, construction materials, and machinery. As per Congo Import Data by Import Globals, gaining knowledge of Congo's import patterns and trading relationships is essential to understanding the country's overall economic well-being and potential for future expansion.
The Republic of the Congo's import volumes grew steadily between 2020 and 2024, reflecting both rising industrial activity and domestic consumption. Imports are essential to the operation of important industries, including manufacturing, energy, and infrastructure. Important products that support the nation's continuing development programs are supplied by major import partners, including China and many European nations. As per Congo Export Data by Import Globals, Congo's changing economic landscape is highlighted, and estimates for its future trade outlook are informed by an examination of key import categories, their values, and strategic trade ties.
General Economic Analysis of Congo
The economy of the Republic of the Congo is largely dependent on its natural resources, especially oil, which contributes significantly to its GDP, government coffers, and export revenues. But historically, as per Congo Import Export Trade Data by Import Globals, the economy has been more susceptible to outside shocks due to changes in the price of oil globally, which has impacted the stability of the economy as a whole. To lessen this reliance, the government has been aggressively pushing industries, including mining, infrastructure development, and agriculture in an effort to diversify the economy. Notwithstanding these initiatives, the nation still faces obstacles such as inadequate infrastructure, a lack of industrial capacity, and the requirement for better governance and an investment-friendly environment to draw in sustained growth.
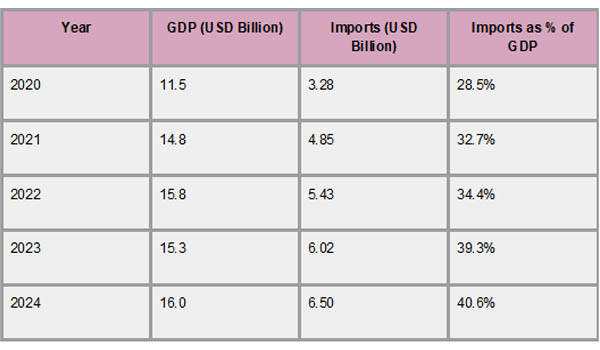
The Congolese economy began to gradually recover and grow between 2020 and 2024, in part because of a stabilization of oil prices and a rise in government spending on infrastructure. Growing imports, as per Congo Import Custom Data by Import Globals, which reflect growing demand for consumer products, construction materials, and machinery, helped the GDP grow gradually. However, elements including inflationary trends, pressures from external debt, and a limited economic base limit the nation's economic growth. To achieve long-term economic resilience and inclusive development, strengthening domestic production capacities, increasing trade diversification, and strengthening fiscal management continue to be top priorities.
Import Data Analysis Of Congo
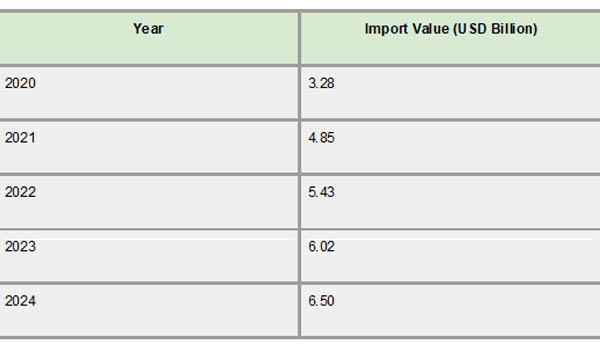
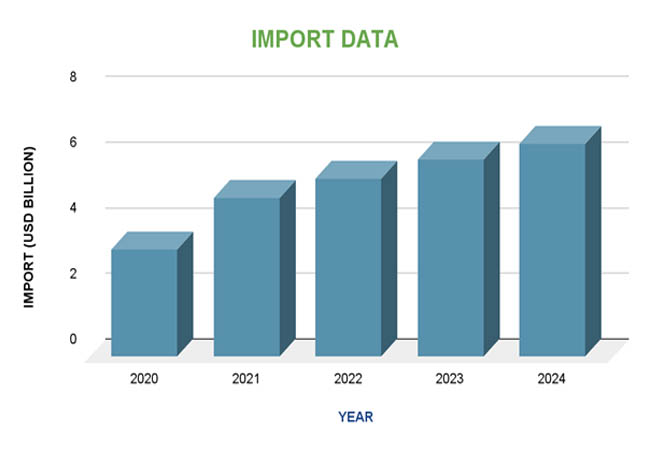
The Republic of the Congo saw a steady increase in import values between 2020 and 2024, which was indicative of a rising need for imported commodities to sustain its economic operations. Imports were anticipated to be worth $3.28 billion in 2020 and are expected to reach $6.50 billion by 2024. This increase highlights the nation's growing industrial needs and consumption, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of almost 16.5%. As per Congo Import Trade Analysis by Import Globals, a noteworthy example of the growing dependence on imports for domestic economic activities is the import-to-GDP ratio, which increased from 28.5% in 2020 to an expected 40.6% in 2024.
 The Republic of the Congo's import structure is broad and includes several areas that are crucial to its growth. Machinery, automobiles, electrical equipment, food, medicine, petroleum products, chemicals, plastics, iron and steel, and textiles are important import categories. Machinery made up 20% of all imports in 2023, with automobiles coming in at 15%, electrical equipment at 12%, and medications at 10%. Together, these industries accounted for 95% of the nation's import value, with a strong increase in machinery, automobiles, and electrical equipment suggesting an emphasis on industrialization and infrastructural development. On the other hand, as per Congo Export Data by Import Globals, sectors like cereals, pharmaceuticals, and petroleum products grew more slowly, indicating possible areas for governmental action to improve local production capacity.
The Republic of the Congo's import structure is broad and includes several areas that are crucial to its growth. Machinery, automobiles, electrical equipment, food, medicine, petroleum products, chemicals, plastics, iron and steel, and textiles are important import categories. Machinery made up 20% of all imports in 2023, with automobiles coming in at 15%, electrical equipment at 12%, and medications at 10%. Together, these industries accounted for 95% of the nation's import value, with a strong increase in machinery, automobiles, and electrical equipment suggesting an emphasis on industrialization and infrastructural development. On the other hand, as per Congo Export Data by Import Globals, sectors like cereals, pharmaceuticals, and petroleum products grew more slowly, indicating possible areas for governmental action to improve local production capacity.
Variety of Import Products
To support its ongoing development projects and domestic requirements, the Republic of the Congo imports a wide range of goods. Construction, energy generation, and industrial development all depend on machinery and mechanical appliances (HS Code 84), which account for a sizable amount of imports. Another significant import category is vehicles (HS Code 87), especially heavy-duty machinery and commercial trucks, which are motivated by the demand for improved transportation infrastructure. Additionally, prominently shown are electrical apparatus and equipment (HS Code 85), which underpin the nation's communication and energy networks. The government's emphasis on infrastructure development and modernization is reflected in these categories, which emphasize the vital role capital goods play in promoting economic growth.
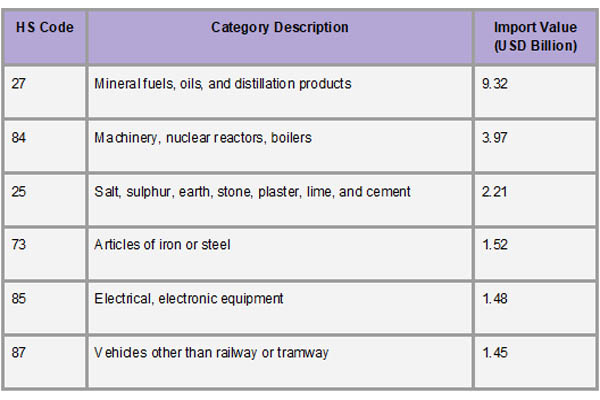
The Congo imports a wide variety of consumer and intermediate items in addition to industrial equipment. Among the essential goods that are imported in significant quantities to satisfy the demands of the expanding population and make up for inadequate domestic production are food items, medications (HS Code 30), and refined petroleum (HS Code 27). For the manufacturing and construction industries, chemicals (HS Code 38), polymers (HS Code 39), iron and steel (HS Code 72), and cement (HS Code 25) are essential. As per Congo Import Data by Import Globals, this wide variety of imports shows how the Republic of the Congo's import portfolio closely reflects both short-term consumer needs and long-term development goals, as well as its larger socioeconomic needs.
Major Import Partners
Strategic alliances with important international economies influence the Republic of the Congo's import environment. As the largest import partner in 2022, China supplied items valued at over $785 million, or 21.6% of the nation's total imports. China primarily exports construction materials, electronics, and machinery to the Congo, which supports the country's infrastructure development objectives. Angola's $408 million (11.2%) imports, mostly of refined petroleum products, came in second only to China. With $350 million (9.6%) in exports, France was the third-largest import partner, supplying a variety of goods such as autos, machinery, and pharmaceuticals. With exports of chemicals, industrial equipment, and medical supplies totaling $238 million (6.6%) and $208 million (5.7%), respectively, Belgium and Germany also made significant appearances.
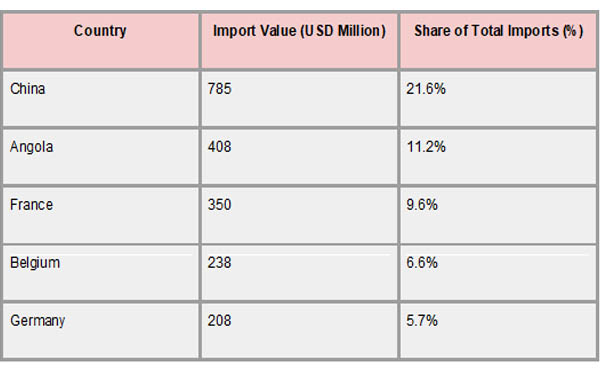
These trade relationships reflect the Republic of the Congo's reliance on foreign partners for essential goods that support its economic activities and development projects. As per Congo Import Trade Statistics by Import Globals, the concentration of imports from a few countries underscores the importance of these partnerships in meeting domestic demand for industrial and consumer products. However, this dependency also highlights potential vulnerabilities, such as exposure to external economic fluctuations and supply chain disruptions. Diversifying import sources and strengthening regional trade ties could enhance the country's economic resilience and reduce over-reliance on specific partners.
Strategic Implications
The import structure of the Republic of the Congo shows strategic priorities for economic modernization and national development. The significant reliance on imports for automobiles, machinery, and electrical equipment shows the government's dedication to industrialization, infrastructure development, and public utility improvement. As per Congo Import Shipment Data by Import Globals, this import behavior is in line with national plans' long-term development objectives, which include bolstering industries like transportation, energy, and construction. However, the nation's limited local manufacturing capacity is also reflected in the necessity to source essential items elsewhere, leaving the economy susceptible to price volatility and interruptions in the global supply chain.
From a geopolitical and trade standpoint, the Congo’s strong import ties with nations like China, France, and neighboring Angola carry both economic advantages and strategic dependencies. While such relationships ensure a steady flow of essential goods, they can also increase external influence over the country’s key sectors. Additionally, the high import bill puts pressure on foreign reserves and can widen the trade deficit if not balanced by sufficient exports. As per the Congo Import Export Trade Analysis by Import Globals, to address these risks, the country must adopt strategic measures such as import substitution through local production, targeted investment in key industries, and trade policy reforms to ensure economic sovereignty and long-term resilience.
Forecast Review
The Republic of the Congo's import panorama from 2020 to 2024 has been characterized by a consistent rise in import values, which reflects the country's rising need for imported commodities to sustain its infrastructural development and economic activity. The expected value of imports increased from $3.28 billion in 2020 to $6.50 billion in 2024. As per Congo Export Import Global Trade Data by Import Globals, this upward trend highlights the nation's growing industrial needs and consumption, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of almost 16.5%. A noteworthy example of the growing dependence on imports for domestic economic activities is the import-to-GDP ratio, which increased from 28.5% in 2020 to an expected 40.6% in 2024.
As per Congo Import Export Global Data, it is anticipated that the Republic of the Congo would maintain its import growth trajectory in the future, propelled by ongoing infrastructure investments and attempts at economic diversification. Investing in domestic sectors to lessen reliance on imports, especially for energy and building supplies, is a crucial factor. Economic growth and import capacity may be supported by putting policies into place that promote commerce and draw in foreign investment. Developing closer relations with nearby nations may facilitate trade and ease logistical obstacles. The nation must, however, also manage possible hazards like inflationary tendencies, pressures from external debt, and a limited economic foundation. To achieve long-term economic resilience and inclusive development, strengthening domestic production capacities, increasing trade diversification, and strengthening fiscal management continue to be top priorities.
Conclusion
In summary, the Republic of the Congo's import patterns between 2020 and 2024 show a developing economy that is highly dependent on outside suppliers for necessities, especially in areas like energy, infrastructure, and industrial growth. Even while the volume and value of imports have been rising gradually, this expansion highlights the urgent need for improved local production, economic diversification, and strategic trade policies. The nation can create a more robust and balanced economy that can survive changes in the global market and promote sustainable growth by investing in self-sufficiency and minimizing its over-reliance on a small number of important partners.
If you are looking for detailed and up-to-date Congo Export Data, you can contact IMPORT GLOBALS.
FAQs
Que. What are the main imported products of the Republic of the Congo?
Ans. The main imports include machinery, vehicles, electrical equipment, refined petroleum, pharmaceuticals, and construction materials.
Que. Who are Congo’s top import partners?
Ans. Congo’s top import partners include China, Angola, France, Belgium, and Germany.
Que. Why are imports increasing in Congo?
Ans. Imports are rising due to growing infrastructure projects, industrial needs, and limited domestic production capacity.
Que. How can Congo reduce its reliance on imports?
Ans. By investing in local industries, improving production infrastructure, and diversifying trade partners.
Que. Where can to obtain detailed Congo Import Data?
Ans. Visit www.importglobals.com or email info@importglobals.com for more information on up-to-date Congo Import Data.
